Secondary Catalogue
Series: Chemistry
Acids and Bases
Acids are sour in taste, while bases are bitter in taste and feel soapy. Acids and bases are present in a variety of things around us.
Addition Reaction of Carbon Compounds
An addition reaction involves a combination of two or more reactants, like ethyne and hydrogen, to form a single product, like ethane. Addition reactions are a characteristic property of unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Adenovirus after 24 Hours
Penetrating the cell's defences, learn about how a virus develops in the nucleus after 24 hours.
Adenovirus Entry
It can be inhaled from a simple sneeze. Discover how adenoviruses attack the cell.
Adenovirus: Journey to the Nucleus
Follow the adenovirus as it journeys to its destination - the nucleus.
Alchemy to the Birth of Chemistry
Deep within the vaults of London's Royal Society, learn about the history that birthed the world's first chemist.
Application of Colloids in Everyday Life
Colloids are heterogeneous mixtures. Colloids play a very important role in our daily lives. Some examples of colloids which we use in our daily lives are - milk, cheese, medicines like antibiotics, milk of magnesia, and solutions soap and detergent.
Atomic Hook-Ups: Types of Chemical Bonds
Atoms are a lot like us - we call their relationships "bonds," and there are many different types. Each kind of atomic relationship requires a different type of energy, but they all do best when they settle into the lowest stress situation possible.
Blueprints for the Cell's Destruction
In its initial entry into the cell, the adenovirus begins to destroy the nucleus.
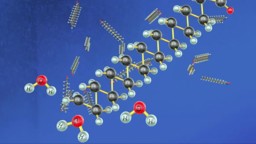
Bonding in Carbon Compounds
Carbon is a versatile element. Its tetravalent nature, to form strong covalent bonds and the property of catenation enables it to form a large number of compounds.
Caustic Soda
Sodium hydroxide is produced by the electrolysis of sodium chloride solution. During electrolysis, hydrogen gas gets evolved at the cathode and chlorine gas gets evolved at the anode.
Cavendish Discovers Hydrogen
The fire of London sparked a journey to discover the powerful properties of flames and more importantly, hydrogen.